About AML/CFT/CPF
-
Money Laundering (ML)
ML refers to the act that attempts to conceal or disguise the true nature of proceeds which are obtained through illicit means, namely criminal proceeds, to evade being detected or arrested by investigative authorities.
*A crime that generates illicit proceeds that become the underlying assets of money laundering is called a predicate offence.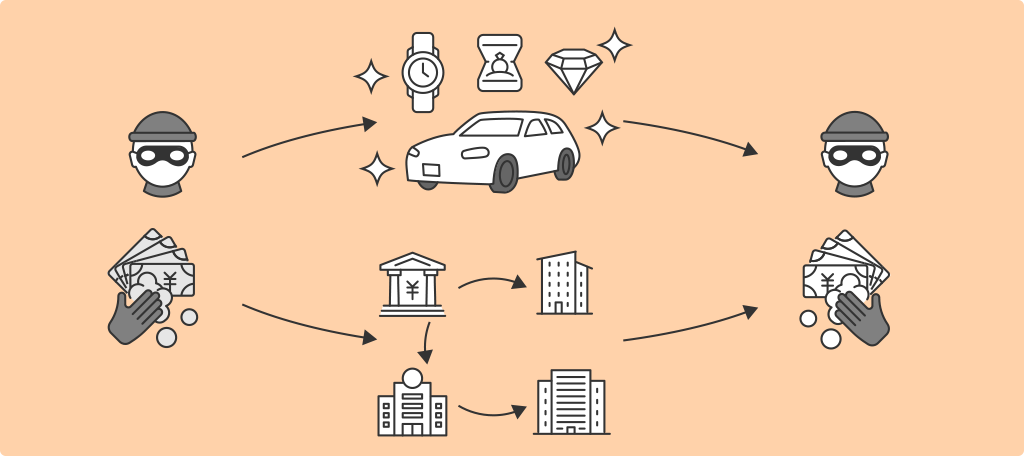
Tip 1
The estimated amount of money laundered globally in one year is approximately 2 - 5% of global GDP.
Source: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC).
-
Terrorist Financing (TF)
TF refers to the collection and provision of funds for terrorist attacks or terrorist organizations/individual terrorists.
-
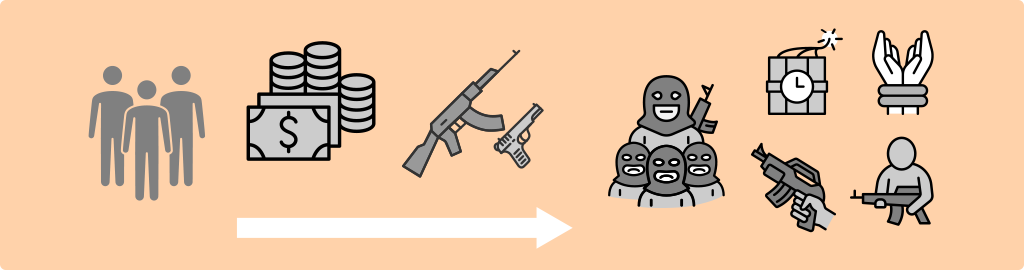
Proliferation Financing (PF)
PF refers to the provision of funds or financial services to parties that are subject to asset freezing and other measures for developing, possessing or exporting weapons of mass destruction (nuclear, chemical, and biological weapons).
Tip 2
As for asset freezing of CPF measures, nearly 400 individuals and entities are designated as those involved in North Korea’s nuclear-related programs and Iranian nuclear activities under the Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Act (FEFTA) and the Terrorist Asset Freezing Act (TAFA) in accordance with United Nations Security Council Resolutions, etc.
Source: Economic sanctions and list of individuals and entities (Ministry of Finance)<Available in Japanese>
- Why are AML/CFT/CPF measures important?
-
If effective AML/CFT/CPF measures are not in place, criminal proceeds will continue to be utilized for further crimes or be used to promote organized crimes or terrorism. ML/TF/PF could also pose a serious threat to sound economic activities and to the integrity of the financial system. Therefore, in order to ensure the safety of citizen’s lives and sound development of economic activities, it is critical to take determined actions of AML/CFT/CPF in cooperation with the international community.
- Overview of ML/TF/PF
-
ML TF PF Sources of funds Criminal proceeds The origins of funds do not matter The origins of funds do not matter Objectives of transfer of funds or financial services To evade the detection of proceeds obtained through illicit means and arrests by investigative authorities by concealing the sources or beneficial owners of the proceeds. To implement terrorist attacks or support terrorist activities To support the proliferation (development, transactions, etc.) of weapons of mass destruction
-
AML/CFT/CPF Measures
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an inter-governmental body established following the Economic Declaration of the 1989 Arche Summit Communique to promote international cooperation on AML. Since the terrorist attacks in the United States in 2001, the FATF has also taken the initiative in promoting CFT globally. Furthermore, the revision of the FATF Recommendations added the FATF’s mandate to cover CPF in February 2012.The FATF operational guidelines are provided in the FATF Mandate approved by ministers in charge of the FATF. The FATF has 38 member jurisdictions (including Japan) and 2 regional organizations and the FATF Plenary meets three times a year, usually in February, June and October.
The FATF publishes the High-Risk Jurisdictions subject to a Call for Action, is often externally referred to as the “black list”, and the Jurisdictions with strategic deficiencies, which is often externally referred to as the “grey list”, to identify jurisdictions that fail to fully comply with international standards and monitor improvements.
FATF-Style Regional Bodies (FSRBs) have been established for 9 regions. Like the FATF members, FSRB members conduct mutual evaluation in line with the FATF standards, which are applied to more than 200 jurisdictions around the world. The Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering (APG) is located in Sydney as the FSRB for the Asia Pacific region, consisting of 42 member jurisdictions, and the largest FSRB in terms of membership numbers and geographical size. Japan has been serving as the Co-Chair of the APG (for a term of approximately two years) since September 2024.
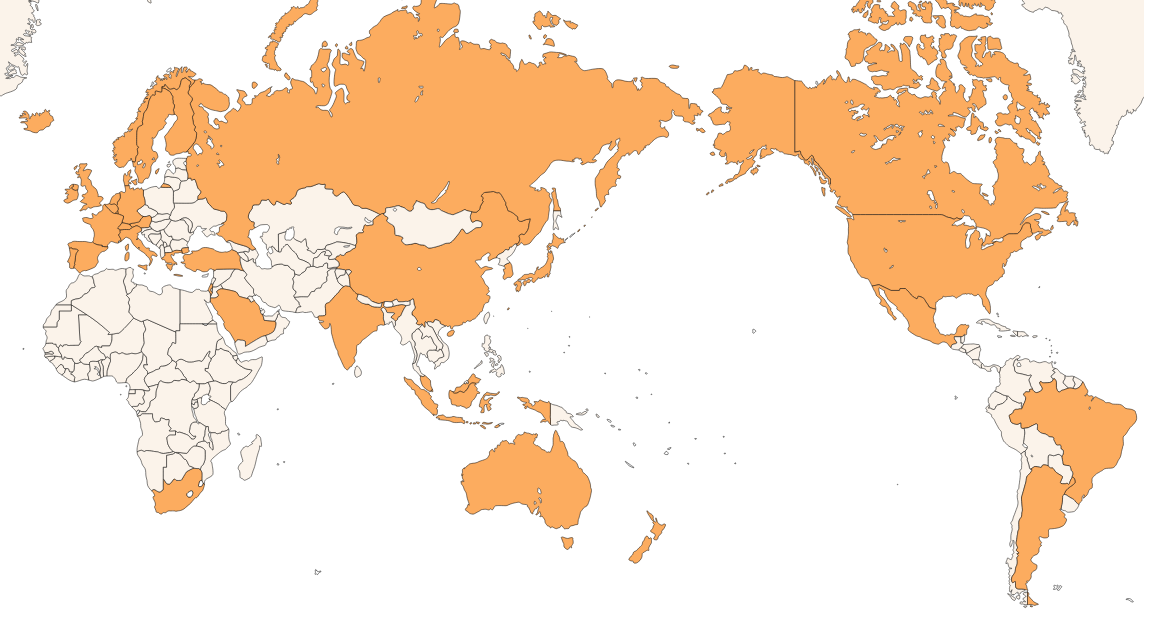
(List of FATF members)
As of September 2024
Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong, China, Iceland, India, Indonesia, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Korea, Luxembourg, Malaysia, Mexico, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Russian Federation (*), Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Türkiye, United Kingdom, United States, European Commission (EC), Gulf Co-operation Council (GCC)
(*) The FATF has decided to suspend the membership of the Russian Federation since February 2023.History of AML/CFT/CPF measures
-
February 2012
Revisions of the FATF 40 Recommendations and 9 Special Recommendations (the FATF integrated both into New 40 Recommendations)
→Applied from the fourth round of mutual evaluation process -
June 2014
Publication of the FATF statement on Japan (The FATF encourages Japan to promptly address AML/CFT/CPF deficiencies.)
-
October 2014
Adoption of the first mutual evaluation reports in the fourth round of FATF evaluation
-
November 2014
Adoption of the amended Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds (APTCP), the amended Act on Punishment of Financing to Offences of Public Intimidation (TF Act), and the Terrorist Asset Freezing Act (TAFA)
-
December 2014
Publication of the national risk assessment (NRA) for the first time
-
May 2016
Adoption of the amended APTCP to require virtual asset exchange service providers to take AML and other measures
-
June 2017
Adoption of the amended Act on Punishment of Organized Crimes and Control of Proceeds of Crime (APOC)
-
February 2018
Establishment of Guidelines for Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism
-
October 2018
Amendments to the FATF Recommendations to address the regulation of virtual assets
-
September 2022
-
December 2022
The Cabinet decision of the Strategy to Make Japan the Safest Country in the World (2022)<Available in Japanese>